Genetically Modified Foods: Safe or Dangerous?
Jason Woods
Cardinal Spellman High School
jwoods@cardinalspellman.org

Introduction:
Genetically modified crops, also known as GM or GMOs (genetically modified, or genetically modified organisms), are plants with altered DNA, giving them greater resistance to herbicides or improved nutritional content. GM foods were originally intended to reduce disease in crops, leading to larger output at less cost and providing enough food for a growing population in a changing environment. However, there are several criticisms of GM foods, including risks to both human health and to our environment. European environmental organizations and public interest groups have been actively protesting against GM foods for months, and recent controversial studies about the effects of genetically-modified corn pollen on monarch butterfly caterpillars have brought the issue of genetic engineering to the forefront of the public consciousness in the U.S. The difficulty of debating the subject of GM foods is they are so new that we don’t really know how they affect the human body. Today, you will determine if GM foods should be allowed for growth and consumption in New York.
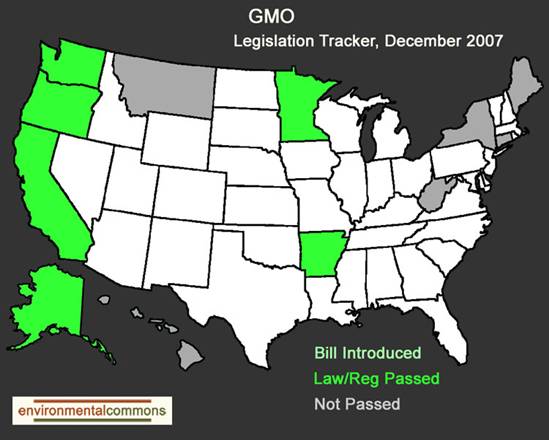
Task:
You are a member of a team researching the risks of GM foods. Your team will conclude whether or not GM foods should be permitted for consumption in New York State. and if so will they be labeled as GMO foods. You will present your reasoning in a PowerPoint presentation to your local congressman, Mr. Banks, so that he may add the banning of GMO foods to his agenda during his next Congressional Meeting.
Process:
In order to complete this task, you will:
1. Assemble a group of 4 students. Each individual from your team will play one of the roles listed below:
· Environmentalist - concerned with problems of the environment, especially with crops developed from genetic engineering that may destroy the balance of nature
· Scientist - concerned with the risks and benefits of food biotechnology
· Consumer Advocate - a concerned citizen who is interested in the health risks that GM foods poses
· Legislator - concerned with the regulations and legislation such as restrictions, labeling etc.
2. Create a PowerPoint presentation of 12 slides using the PPA to:
· Explain the major issues about GM foods (Must include at least one specific GM food)
· Analyze the risks and benefits of GM foods
· Decide if stricter regulations are needed; give reasons for your opinion.
3. Share your knowledge of the treatment you chose with your classmates during a 5 minute oral presentation
4. Address six steps of the PPA format by completing a worksheet for each step
The steps of the PPA are as follows:
Step 1: Define the Social Problem : Use the resources provided to research the benefits and risks of GM foods (Worksheet 1)
Step 2: Gather Evidence of the Problem : Find evidence that a problem exists with the use of GM foods either due to health or environmental concerns (Worksheet 2)
Step 3: Identify Causes of the Problem : Identify the causes of the Problems due to GM foods (Worksheet 3)
Step 4: Evaluate Existing Public Policies : Evaluate the existing the policy with regard to the growth and sale of GM foods in the U.S. (Worksheet 4)
Step 5: Develop Public Policy Solutions : Develop possible public policy solutions to the problems caused by GM foods (Worksheet 5)
Step 6: Select the Best Public Policy Solution : Select the most feasible and effective solution to the problem (Worksheet 6)

Resources:
Use the following links as resources to help guide you through this assignment:
· FDA: Risks and Benefits of GM foods
· Organic Consumers Association
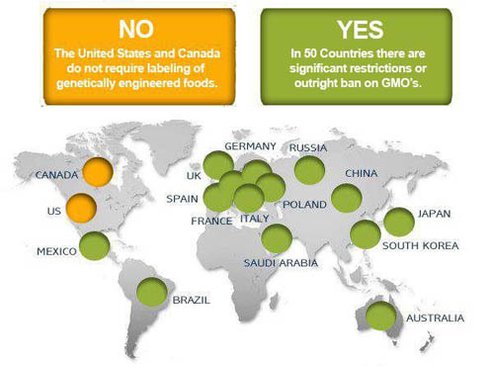
Evaluation:
Each student will be evaluated on both the oral and PowerPoint presentations.
1. Oral Presentation Rubric
|
Category |
Excellent (4) |
Good (3) |
Satisfactory (2) |
Unsatisfactory (1) |
|
Presentation Skills |
Student makes eye contact with audience; well prepared. |
Student acknowledges audience at times; shows some preparedness. |
Student makes some eye contact with audience; relies heavily on index cards; minimum rehearsal. |
Student does not make eye contact; demonstrates no preparedness. |
|
Group Participation |
Every member of the group speaks for equal amounts of time. |
Every member of the group speaks; time not split evenly. |
Most members of the group speak; time not split evenly. |
Only one member of the group speaks; other members do not participate. |
|
Key Vocabulary Words |
Incorporates all necessary vocabulary associated with issue; explains any new words to audience. |
Incorporates some vocabulary words; explains any new words to audience. |
Incorporates some vocabulary words; does not explain new words to audience. |
Does not incorporate vocabulary words. |
|
Content |
All information related to topic; all steps of PPA incorporated successfully. |
Most information related to topic; most steps of PPA incorporated successfully. |
Some information related to topic; some steps of PPA incorporated successfully. |
Most information not related to topic; no steps of PPA incorporated successfully. |
2) PowerPoint Presentation Rubric
|
Category |
Excellent (4) |
Good (3) |
Satisfactory (2) |
Unsatisfactory (1) |
|
Organization |
Slides are easily legible; arranged in a sensible manner. |
Slides are easily legible; arrangement of some slides not cohesive. |
Some slides not clearly legible; arrangement of slides not cohesive. |
Slides not clearly legible; no clear arrangement of slides. |
|
Sources |
Sources cited correctly; all sources are reliable. |
Sources cited with few errors; sources are reliable. |
Sources cited with many errors; some sources are unreliable. |
Sources cited incorrectly; all sources unreliable. |
|
Information |
All slides relate to topic; clear attempt to solve the issue. |
Most slides relate to topic; some attempt to solve the issue. |
Most slides relate to topic; vague attempt to solve the issue. |
Few slides relate to topic; no attempt to solve the issue. |
|
PPA Incorporation |
All six steps of the PPA addressed successfully. |
Five of the six steps of the PPA addressed successfully. |
Four of the six steps of the PPA addressed successfully. |
Three or fewer steps of the PPA addressed successfully. |
Breakdown of Points
32 – 26 = A
25 -19 = B
18 – 12 = C
11 – 5 = D
5 – 0 = F

Conclusion:
At the end of this activity you should be able to defend your position based on the research performed regarding risks and benefits of GM foods. Successful completion of this project should help you inform others about the controversy associated with GM foods. It should also provide you with enough information and knowledge to change the minds of those who are in favor of GM foods. Increasing awareness of the dangers of GM foods is necessary if we hope to curtail their use and consumption. Congratulations on your hard work and increasing your knowledge of the world of science.
Living Environment Standards
Standard 4
Key Idea 2:
● Organisms inherit genetic information in a variety of ways that result in continuity of structure and function between parents and offspring.
● Organisms from all kingdoms possess a set of instructions (genes) that determines their characteristics. These instructions are passed from parents to offspring during reproduction. Students are familiar with simple mechanisms related to the inheritance of some physical traits in offspring. They are now able to begin to understand the molecular basis of heredity and how this set of instructions can be changed through recombination, mutation, and genetic engineering.
● The inherited instructions that are passed from parent to offspring exist in the form of a code. This code is contained in DNA molecules. The DNA molecules must be accurately replicated before being passed on. Once the coded information is passed on, it is used by a cell to make proteins. The proteins that are made become cell parts and carry out most functions of the cell.
● Throughout recorded history, humans have used selective breeding and other biotechnological methods to produce products or organisms with desirable traits. Our current understanding of DNA extends this to the manipulation of genes leading to the development of new combinations of traits and new varieties of organisms.
PERFORMANCE INDICATOR 2.2
Explain how the technology of genetic engineering allows humans to alter genetic makeup of organisms.
Major Understandings
2.2a For thousands of years new varieties of cultivated plants and domestic animals have resulted from selective breeding for particular traits.
2.2b In recent years new varieties of farm plants and animals have been engineered by manipulating their genetic instructions to produce new characteristics.
2.2c Different enzymes can be used to cut, copy, and move segments of DNA. Characteristics produced by the segments of DNA may be expressed when these segments are inserted into new organisms, such as bacteria.
2.2d Inserting, deleting, or substituting DNA segments can alter genes. An altered gene may be passed on to every cell that develops from it.
2.2e Knowledge of genetics is making possible new fields of health care; for example, finding genes which may have mutations that can cause disease will aid in the development of preventive measures to fight disease. Substances, such as hormones and enzymes, from genetically engineered organisms may reduce the cost and side effects of replacing missing body chemicals.
English Standards
Standard 2: Language for Literary Response and
Expression
Students will read and listen to oral, written, and electronically produced
texts and performances from American and world literature; relate texts and
performances to their own lives; and develop an understanding of the diverse
social, historical, and cultural dimensions the texts and performances
represent. As speakers and writers, students will use oral and written language
that follows the accepted conventions of the English language for
self-expression and artistic creation.
E1c Reads, understands and produces written and oral work.
E3b The student participates in group meetings.
E4b The student analyzes and revises the work to make it suitable for the audience.
S5f Students work individually and in teams to collect and share information and ideas.
S7b The student argues from evidence.
S7e Students communicates in a form suited for the audience.
A2a Student makes an oral presentation of project plan.
Mathematics, Science and Technology Standards
Standard 5: Technology
Students will apply technological knowledge and skills to design, construct, use and evaluate products and systems to satisfy human and environmental needs.